An Integrated MCDM approach
in ArcGIS
ABOUT COURSE
In this online course, you can learn the complete process (A-Z) from scratch to production. How to select parameters and why, download raster and vector data, processing data, images in ArcGIS environment, justification of variables, step by step guide of SPI, CRITIC, WASPAS, and SAW models in excel, produced prediction map applying CRITIC, WASPAS, and SAW methods in Drought Vulnerability zonation using ArcGIS. Moreover, you will also learn validation of the susceptibility map using advanced techniques such as MAE, MSE, RMSE, ROC-AUC.
SPI (Standardized Precipitation Index) is a widely used index to characterize meteorological drought on a range of timescales. On short timescales, the SPI is closely related to soil moisture, while at longer timescales, the SPI can be related to groundwater and reservoir storage. The SPI can be compared across regions with markedly different climates. It quantifies observed precipitation as a standardized departure from a selected probability distribution function that models the raw precipitation data. The raw precipitation data are typically fitted to gamma or a Pearson Type III distribution and then transformed to a normal distribution. The SPI values can be interpreted as the number of standard deviations by which the observed anomaly deviates from the long-term mean. The SPI can be created for differing periods of 1-to-36 months, using monthly input data. For the operational community, the SPI has been recognized as the standard index that should be available worldwide for quantifying and reporting meteorological drought.
CRITIC (Criteria Importance Through Inter-criteria Correlation) a useful method that identifies the objective weight of MCDM problems based on contrast intensity and the conflicting character of the evaluation criteria proposed by Diakoulaki, Danae, George Mavrotas, and Lefteris Papayannakis (1995).
WASPAS method (weighted aggregated sum product assessment) is one of the MCDM methods. It was developed by Zavadskas et al. The WASPAS method is a unique combination of the Weighted Sum Model (WSM) and Weighted Product Model (WPM) which are two well-known MCDM methods. The WSM method determines the overall score of an alternative as a weighted sum of the criteria values while WPM determines the score of an alternative as a product of the scale rating of each criterion to a power equal to the weight of a given criterion. In addition to these methods, WASPAS tries to reach the highest accuracy of estimation by optimizing weighted aggregated function
SAW (Simple Additive Weighting) method is a well-known method relying on the linear utility function for multi-criteria evaluation (Hwang, Yoon 1981, Rozman et al. 2016, Vico 2017). Churchman and Ackoff (1954) first utilized the SAW method to cope with a portfolio selection problem. The SAW method is probably the best known and widely used method for multiple attribute decision-making (MADM). Because of its simplicity, SAW is the most popular method in MADM problems
After completing this course, you will be efficiently able to process, predict, and validate any data related to hazard, vulnerability, risk, and suitability assessment using the CRITIC, WASPAS, and SAW models.
Keywords: Excel, ArcGIS, R-studio, SPI, CRITIC, WASPAS, SAW, Drought, Mapping, Prediction
Who this course is for
Students, researchers and professionals of Natural hazards, Environmental Science, Engineering, Remote Sensing and Geography.
Students, researchers and professionals who are interested in multi-criteria decision making and risk analysis using GIS Data.
Students, researchers and professionals who work on: Hazards, vulnerability and risk [flooding, landslides, drought], susceptibility [Groundwater potentiality, vulnerability] and Suitability [Agricultural suitability, Irrigation suitability].
Anyone interested in learning the Structured Decision-Making Using Step by Step Approach.
Are there any course requirements or prerequisites?
Basic Knowledge of Microsoft Excel
No statistical background needed
Basics knowledge in ArcGIS software and QGIS is optional
Interest in GIS prediction maps using real-life Data
Course Curriculum
- 1. Introduction to Multicriteria Decision Making Model
- 2. Literature Review
- 3. Understanding of Landslide
- 4. Understanding of Landslide Susceptibility Zonation
- 5. Selection of relevant Criteria
- 1. How to select study area
- 2. How to prepare location map of the study area
- 3. How to prepare flow diagram
- 1. Download Satellite data
- 2. Download Vector data
- 3. Preparation of topographic indices
- 4. Preparation of remote sensing indices
- 5. Preparation of Climatic indices
- 1. Understanding SPI
- 2. Data download
- 3. Data Processing
- 4. Calculation of SPI using R software
- 5. Calculation of drought frequency
- 6. Calculation of drought intensity
- 7. Thematic layers preparation
- 1. Introduction to WASPAS
- 2. Steps Involved in WASPAS
- 3. WASPAS: Drought vulnerability using Microsoft Excel
- 4. Model runs in ArcGIS
- 5. Area Calculation of each class
- 6. Export maps
- 1. Introduction to SAW
- 2. Steps Involved in SAW
- 3. SAW : Drought vulnerability using Microsoft Excel
- 4. Model runs in ArcGIS
- 5. Area Calculation of each class
- 6. Export maps
- 1. Introduction to CRITIC
- 2. Steps Involved in CRITIC
- 3. CRITIC: Drought vulnerability using Microsoft Excel
- 4. CRITIC- WASPAS: Drought vulnerability using Microsoft Excel
- 5. CRITIC- SAW: Drought vulnerability using Microsoft Excel
- 6. Model runs in ArcGIS
- 7. Area Calculation of each class
- 8. Export maps
- 1. Mean Absolute Error (MAE)
- 2. Mean Squared Error (MSE)
- 3. Root-Mean-Squared Error (RMSE)
- 4. ROC-AUC
- 1. Preparation of Tables
- 2. Preparation of Figures
- 3. Preparation of final layout
- 1. Feedback
- 2. Final layout of article
Benefit of Online International Workshop
- Step by step procedure from data download, handling, selection, produce prediction map to validation
Comprehensive understanding of SPI, CRITIC, WASPAS, and SAW models and its Interface with Various Decision-Making Interfaces
- Instructors continuous support, taking your hand step-by-step to develop high-quality prediction maps using real data
- Live WhatsApp Chatting with the instructor
- 1:1 Sessions with experts
- Lifetime Access
- Any time watch recorded videos

Ready to enroll in Online International Workshop?
An Integrated MCDM approach for Drought Vulnerability Assessment in ArcGIS
An Integrated MCDM approach for Drought Vulnerability Assessment in ArcGIS
Other GIS Courses
e-Workshop
on
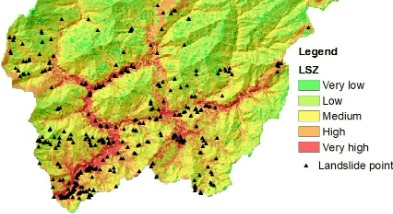
An Ensemble of Evidence Belief Function (EBF) with Frequency Ratio (FR) for GIS-based landslide prediction in ArcGIS
Live 16/07/22 to 27/08/22
INR. 10000.00 USD. 150.00
Enroll nowCertificate Course
On
An Ensemble of Evidence Belief Function (EBF) with Frequency Ratio (FR) for GIS-based landslide prediction in ArcGIS
An Ensemble of Evidence Belief Function (EBF) with Frequency Ratio (FR) for GIS-based landslide prediction in ArcGIS
In this online workshop and live practice, you can learn the complete process (A-Z) from scratch to production. How to select parameters and why, download raster and vector data, processing data, images in ArcGIS environment, justification of variables, step by step guide of Dempster-Shafer theory of EBF and FR models, produced prediction map applying combined EBF and FR methods in Landslide prediction zonation using ArcGIS. Moreover, you will also learn validation of the susceptibility map using advanced techniques such as success rate curve and prediction rate curve.
After completing this course, you will be efficiently able to process, predict, and validate any data related to hazard, vulnerability, risk, and suitability assessment using the EBF and FR models.

Certificate Course on
Groundwater potentiality and stress zonation using TOPSIS, VIKOR and EDAS models in ArcGIS
INR. 10000.00
USD. 150
Certificate Course
On
Groundwater potentiality and stress zonation using TOPSIS, VIKOR, and EDAS models in ArcGIS
In this online certificate course, you can learn the complete process (A-Z) from scratch to production. How to select parameters and why, download raster and vector data, processing data, images in ArcGIS environment, justification of variables, step by step guide of TOPSIS, VIKOR and EDAS in excel, produced prediction map applying these methods in groundwater potentiality and stress zonation using ArcGIS. Moreover, you will also learn validation of the potentiality map in ArcGIS software.
Certificate Course on Flood Hazards, Vulnerability and Risk Assessment using Analytical Hierarchy Process in ArcGIS
In this course, you can learn the complete process (A-Z) from scratch to production. How to select parameters and why, download raster and vector data, processing data, images in ArcGIS environment, justification of variables, step by step guide of Analytic Hierarchy Process (AHP) in excel, produced prediction map applying AHP method in hazard, vulnerability, and risk using GIS. Moreover, you can also learn sensitivity analysis in ArcGIS and validation of the susceptibility map in SPSS software.
Analytic Hierarchy Process (AHP) is the most powerful multi-criteria decision-making and Problem-Solving method first introduced by Saaty in 1980. In short, it is used for ranking the attributes to select the optimal attribute based on the hierarchical structure of goal at the top level, criteria at the second level, and alternative at third level
After completing this course, you will be efficiently able to process, predict, and validate any data related to hazard, vulnerability, risk, and suitability assessment using the Analytic Hierarchy Process (AHP).

Certificate Course
Flood Hazards, Vulnerability and Risk Assessment using Analytical Hierarchy Process in ArcGIS
INR. 10000.00
USD. 150
Why Learn With us?
Over two decades of experience and expertise in teaching Tech and coding helping students develop their tech skills for higher performance, better careers and growth in companies.

Benefit of taking this course?
World Class Teachers
Get certified with our premium courses and get started on your journey to a brand new career altogether
Certifications
Get certified with our premium courses and get started on your journey to a brand new career altogether
Students Community
Get certified with our premium courses and get started on your journey to a brand new career altogether
Live session
Get certified with our premium courses and get started on your journey to a brand new career altogether